The field of dentistry is undergoing a monumental shift, driven by groundbreaking new materials and advanced technologies. These innovations are not merely incremental improvements; they are fundamentally reshaping how oral healthcare is delivered, experienced, and perceived. From revolutionary therapies harnessing the body’s own regenerative powers to sophisticated algorithms that mimic human cognitive processes, the future of dental care promises enhanced patient experiences, superior treatment outcomes, and a redefinition of standard dental practices. This article will explore these advancements, offering a detailed glimpse into the transformative changes poised to define the next era of dentistry, reflecting the standards and expectations of 2025 and beyond.
Regenerative Dentistry: The Dawn of Biological Healing
One of the most exciting frontiers in dental innovation is the burgeoning field of regenerative dentistry. This approach centers on utilizing the body’s inherent healing mechanisms to repair or replace damaged tissues and structures within the oral cavity. The focal point of this revolution lies in stem cell research and its potential to revolutionize treatment modalities.
Unlocking the Potential of Dental Stem Cells
Dental stem cells, with their unique regenerative capabilities, are sourced from various locations within the oral environment. These sources include:
- Dental pulp of permanent teeth: A rich source of mesenchymal stem cells.
- Exfoliated deciduous teeth (baby teeth): Easily accessible and possessing high proliferative potential.
- Periodontal ligament: Located around the tooth root, crucial for tooth support and regeneration.
- Apical papilla: Found at the root tip of developing teeth, offering significant regenerative capacity.
- Dental follicle: Surrounding developing teeth, involved in tooth and bone formation.
These stem cells can be harnessed for a variety of applications, including:
- Tissue Engineering: Creating functional dental tissues in vitro for implantation.
- Cell-Based Therapies: Injecting stem cells directly into damaged sites to stimulate regeneration.
- Growth Factor Delivery: Utilizing stem cells to deliver targeted growth factors, accelerating healing and tissue repair.
The ultimate goal of regenerative dentistry is to achieve complete tooth regeneration, effectively eliminating the need for traditional restorative solutions such as implants, bridges, and dentures. This represents a paradigm shift, moving away from artificial replacements towards biologically integrated, self-repairing dental structures.
The Role of Gene Therapy
Alongside stem cell research, gene therapy holds promise in regenerative dentistry. By introducing specific genes into cells, researchers aim to stimulate the production of proteins that promote tissue regeneration. This could lead to:
- Enhanced bone regeneration for implant placement
- Stimulation of enamel formation to repair damaged teeth
- Improved healing of gum tissues after surgery
The Digital Revolution: 3D Printing and Artificial Intelligence
The integration of digital technologies is transforming virtually every aspect of dental practice, from diagnosis and treatment planning to fabrication and execution. Two key pillars of this digital revolution are 3D printing and artificial intelligence (AI).
3D Printing: Precision Manufacturing in the Dental Office
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, enables the creation of three-dimensional objects from digital designs with unparalleled precision and efficiency. In dentistry, 3D printing is used to fabricate a wide range of products, including:
- Dental Models: Accurate replicas of a patient’s dentition for diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Surgical Guides: Precisely fitted guides for implant placement and other surgical procedures.
- Orthodontic Aligners: Clear, custom-made aligners for teeth straightening.
- Crowns and Bridges: Restorations with exceptional fit and aesthetics.
- Provisional Restorations: Temporary crowns and bridges for immediate use.
The benefits of 3D printing in dentistry are numerous:
- Enhanced Precision: Digital designs translate into highly accurate physical objects.
- Customization: Treatments tailored to the unique anatomy and needs of each patient.
- Efficiency: Streamlined workflows and reduced turnaround times.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduced material waste and labor costs.
Artificial Intelligence: Augmenting Human Expertise
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly emerging as a powerful tool for augmenting the capabilities of dental professionals. AI algorithms are being developed and implemented to:
- Improve Diagnostic Accuracy: Analyzing radiographs and other diagnostic images to detect subtle anomalies.
- Optimize Treatment Planning: Developing personalized treatment plans based on comprehensive data analysis.
- Enhance Surgical Precision: Assisting with surgical procedures through real-time guidance and robotic assistance.
- Automate Administrative Tasks: Streamlining appointment scheduling, billing, and insurance claims processing.
AI-powered tools are not intended to replace human dentists but rather to enhance their skills and improve the quality of care they provide. By automating routine tasks and providing data-driven insights, AI allows dentists to focus on complex cases and patient interaction, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
Virtual and Augmented Reality in Dentistry
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are starting to make inroads into dental education and patient communication. VR can simulate complex procedures for training purposes, while AR can overlay digital information onto the real world during treatment, providing dentists with enhanced visualization and guidance.
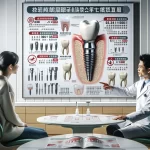
Advanced Materials: The Building Blocks of Tomorrow’s Dentistry
The development of advanced materials is crucial for the continued progress of dental innovations. These materials offer improved properties, enhanced biocompatibility, and expanded functionalities compared to traditional dental materials.
Nanomaterials: Strength, Aesthetics, and Antimicrobial Properties
Nanomaterials, with their ultra-fine particle sizes, exhibit unique properties that make them ideal for dental applications. Nanomaterials are being incorporated into:
- Dental Composites: Enhancing strength, durability, and aesthetics of fillings.
- Bone Grafting Materials: Promoting faster and more complete bone regeneration.
- Dental Implants: Improving osseointegration and reducing the risk of infection.
- Adhesives: Strengthening the bond between dental materials and tooth structure.
- Antimicrobial Coatings: Preventing the growth of bacteria on dental surfaces.
Biocompatible Coatings: Seamless Integration with the Body
Biocompatible coatings are designed to promote faster and more complete integration of dental implants and other devices with the surrounding tissues. These coatings can:
- Enhance osseointegration of dental implants
- Reduce the risk of inflammation and infection
- Promote tissue regeneration around implants
- Improve the long-term stability of dental restorations
Bioactive Materials
Bioactive materials can interact with the oral environment to stimulate tissue repair and regeneration. These materials release ions that promote the formation of new bone and tooth structure, aiding in the healing process.
Patient-Centric Innovations: Comfort, Convenience, and Accessibility
Beyond technological advancements, the next generation of dental innovations places a strong emphasis on patient-centric care. This involves developing technologies and approaches that enhance patient comfort, convenience, and accessibility to dental services.
Minimally Invasive Techniques: Preserving Natural Tooth Structure
Minimally invasive dentistry aims to preserve as much natural tooth structure as possible during restorative procedures. This approach utilizes:
- Air abrasion
- Microscopic dentistry
- Biomimetic materials
By minimizing the removal of healthy tooth structure, minimally invasive techniques can prolong the life of teeth and reduce the need for more extensive treatments in the future.
Pain Management Technologies: Minimizing Discomfort
Advances in pain management technologies are making dental visits more comfortable for patients. These include:
- Computer-controlled local anesthesia delivery systems
- Topical anesthetics with improved efficacy
- Laser therapy for reducing post-operative discomfort
- Sedation dentistry options for anxious patients
Teledentistry: Bringing Dental Care to Remote Locations
Teledentistry uses telecommunications technology to deliver dental care remotely. This can include:
- Virtual consultations
- Remote monitoring of treatment progress
- Online education and training
Teledentistry can improve access to care for patients in rural areas, those with mobility limitations, and those who have difficulty accessing traditional dental offices.
Personalized Medicine in Dentistry
The future of dentistry is moving towards personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the individual patient’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and oral health status. This includes:
- Genetic testing to identify risk factors for dental diseases
- Custom-made dental implants and prosthetics
- Personalized oral hygiene recommendations
Eco-Conscious Dentistry: Minimizing Environmental Impact
The dental industry is increasingly embracing sustainable practices to minimize its environmental impact. This includes:
Green Products: Reducing Waste and Pollution
- Biodegradable toothbrushes and floss: Made from renewable resources that decompose naturally.
- Eco-friendly dental materials: Formulated with non-toxic and sustainable ingredients.
- Digital radiography: Eliminating the need for film processing chemicals.
Clinic Initiatives: Conserving Resources
- Water conservation measures
- Energy-efficient equipment and lighting
- Recycling programs
- Waste reduction strategies
By adopting eco-conscious practices, dental professionals can contribute to a healthier planet while providing high-quality care.
Transforming Dental Education: Preparing for the Future
The rapid pace of innovation in dentistry requires a transformation in dental education. Dental schools are incorporating:
Immersive Learning Technologies
- Virtual reality simulations
- Haptic feedback devices
Online Learning Modules
- Interactive lectures
- Case-based learning
Specialized Programs
- Digital dentistry
- Regenerative dentistry
- Implant dentistry
These educational reforms ensure that future dental professionals are well-equipped to embrace new technologies and deliver the highest standards of care.
Continuing Education and Training
Lifelong learning is essential for dental professionals to stay up-to-date with the latest advancements. Continuing education courses, workshops, and conferences provide opportunities for dentists to expand their knowledge and skills.
Conclusion: A New Era of Oral Healthcare
The next generation of dental innovations promises to usher in a new era of oral healthcare, characterized by regenerative therapies, digital precision, advanced materials, and patient-centric approaches. As these innovations continue to evolve and mature, patients can expect treatments that are more effective, less invasive, and more personalized than ever before. The dental practice of tomorrow will seamlessly integrate cutting-edge technologies with compassionate care, ultimately leading to healthier smiles and improved quality of life for all.
What are the next generation of dental innovations?
The next generation of dental innovations includes advancements in materials used for dental procedures. This includes the use of bioactive glass in dental fillings, which has the potential to prolong the life of fillings, and the development of new, more durable materials for dental implants and crowns.
How are these new materials improving dental procedures?
These new materials are improving dental procedures by offering greater durability, improved aesthetics, and potential health benefits. For example, bioactive glass in dental fillings not only matches the color of natural teeth but also releases fluoride, calcium, and phosphate, which can help protect the tooth.
What is bioactive glass and how is it used in dentistry?
Bioactive glass is a type of glass that interacts with the body to stimulate healing. In dentistry, it’s used in dental fillings to release minerals that can help protect the tooth from decay. It’s also used in other dental products like toothpaste and sealants.
Are these new materials safe?
Yes, these new materials have been extensively tested for safety and efficacy. Bioactive glass, for example, has been used in medicine for decades and has a proven track record of safety. As with any dental material, your dentist will consider your individual health needs when recommending these products.
How can I find out if these new materials are right for me?
If you’re interested in these next-generation dental innovations, talk to your dentist. They can provide more information about these materials and help you decide if they’re a good fit for your dental needs.