It’s 2 AM, and you’re jolted awake by a sharp, throbbing pain in your jaw. As you fumble for relief, questions race through your mind: What’s causing this? How serious is it? Can it wait until morning? You’re not alone; dental pain affects millions worldwide, with recent studies showing that up to 57% of adults experience toothaches each year. This comprehensive guide will help you understand, manage, and prevent dental pain while leveraging the latest advancements in dental care for 2024.
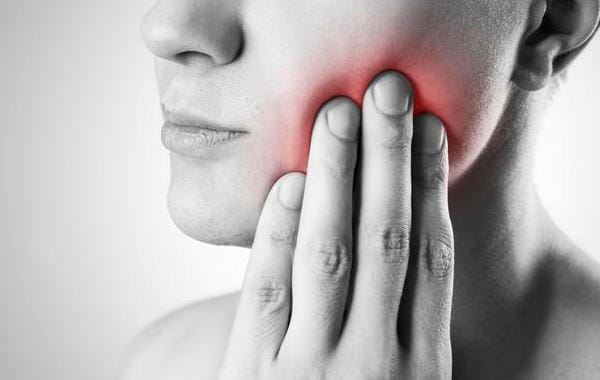
Understanding Dental Pain
Dental pain can range from a mild annoyance to debilitating discomfort. To effectively address it, understanding its nature and origins is crucial.
Types of Dental Pain
Dental pain manifests in various ways, including:
Sharp and shooting: Sudden bursts of pain that can be triggered by temperature changes or certain foods.
Dull and constant: A persistent ache that may indicate underlying issues like decay or gum disease.
Throbbing: A rhythmic pain often associated with infections or severe decay.
Temperature sensitivity: Discomfort when consuming hot or cold items.
Pain when biting or chewing: Indicates potential fractures or cavities.
Common Causes of Dental Pain
Understanding the root causes of dental pain can help in seeking timely treatment. Here are some common culprits:
Tooth decay: Bacteria produce acids that erode enamel, leading to cavities.
Gum disease: Inflammation caused by bacterial infection can result in pain and bleeding.
Dental trauma: Injuries from accidents or sports can fracture teeth.
Tooth sensitivity: Worn enamel or exposed roots increase sensitivity to temperature changes and certain foods.
Infections: Abscesses can form when bacteria invade the tooth or gums.
Did You Know? The human mouth contains over 6 billion bacteria, some of which contribute to tooth decay and gum disease.
Decoding Your Symptoms
Understanding your symptoms is the first step toward relief. Let’s explore the most common causes of dental pain and their telltale signs.
1. Tooth Decay and Cavities
Symptoms:
- Sharp pain when eating sweet, hot, or cold foods
- Visible holes or pits in teeth
- Brown, black, or white staining on tooth surfaces
What’s Happening: Bacteria in your mouth produce acid that erodes tooth enamel, creating cavities. As decay progresses, it can reach the sensitive inner layers of the tooth, causing pain.
2. Gum Disease
Symptoms:
- Swollen, red, or tender gums
- Bleeding when brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums
What’s Happening: A bacterial infection in the gums leads to inflammation and bleeding. If left untreated, this can result in tooth loss.
Expert Opinion: “Early intervention in gum disease can prevent up to 80% of tooth loss cases,” says Dr. Emily Chen, periodontist at UCLA School of Dentistry.
3. Tooth Fractures and Injuries
Symptoms:
- Sharp pain when biting or chewing
- Sensitivity to temperature changes
- Visible cracks or chips in the tooth
What’s Happening: Trauma from accidents or biting hard objects can cause fractures that expose sensitive inner layers of the tooth.
4. Tooth Sensitivity
Symptoms:
- Brief, sharp pain with hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods
- Discomfort during brushing or flossing
What’s Happening: Worn enamel or exposed tooth roots heighten sensitivity to temperature changes and certain foods.
5. Oral Infections and Abscesses
Symptoms:
- Severe, persistent throbbing pain
- Swelling in the face or cheek
- Fever
- Sensitivity to touch and temperature
What’s Happening: Bacterial infections can lead to pus accumulation in tooth roots or gums, resulting in painful abscesses.
Immediate Relief Strategies
While professional dental care is often necessary for long-term solutions, these home remedies and over-the-counter options can provide temporary relief:
Home Remedies
| Remedy | Instructions |
|---|---|
| Saltwater rinse | Dissolve 1/2 teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water; rinse for 30 seconds. |
| Cold compress | Apply to the outside of the cheek near the affected area for 15–20 minutes. |
| Peppermint tea bags | Apply a cooled used tea bag to the affected area for soothing relief. |
Over-the-Counter Solutions
| Solution | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Pain relievers | Ibuprofen or acetaminophen manage pain and reduce inflammation. |
| Topical anesthetics | Gels containing benzocaine temporarily numb the affected area. |
| Clove oil | Apply directly to the affected tooth for natural pain relief. |
Caution: These methods provide temporary relief; persistent pain requires professional evaluation.
When to Seek Professional Help
While home remedies can provide temporary relief, certain situations require immediate professional attention:
Emergency Situations
You should seek immediate dental care if you experience:
Severe, persistent pain lasting more than 1–2 days
Swelling in the face or cheek
Fever accompanying dental pain
Trauma resulting in a broken or knocked-out tooth
Difficulty breathing or swallowing
Dental Procedures for Pain Relief
When you visit a dentist for a toothache, they may recommend treatments based on your diagnosis:
Fillings: For cavities and minor decay.
Root canal therapy: For severe decay or infection.
Dental crowns: For cracked or weakened teeth.
Scaling and root planing: For gum disease.
Tooth extraction: For severely damaged or infected teeth.
Technological Advancements in Dental Care (2024)
The field of dentistry continues to evolve with new ways to diagnose, treat, and prevent dental pain:
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| AI-powered diagnostic tools | Advanced imaging detects issues earlier with greater accuracy. |
| 3D printed dental restorations | Custom-made crowns and bridges produced on-site for faster treatment. |
| Regenerative therapies | Stem cell treatments show promise in regenerating damaged tooth tissue. |
| Teledentistry | Virtual consultations allow for preliminary diagnoses—especially useful after hours. |
Did You Know? A recent study showed that AI-assisted diagnoses have an accuracy rate of up to 95%, often catching issues that human dentists might miss.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing dental pain is always preferable to treating it. Here are key strategies to maintain optimal oral health:
Daily Oral Care Routine
Implementing a consistent oral care routine is essential:
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss at least once a day.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash.
Proper Brushing Technique:
Hold your brush at a 45-degree angle to your gums and use gentle circular motions while brushing all surfaces for at least two minutes.
Diet and Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a balanced diet contributes significantly to oral health:
Limit sugary and acidic foods.
Avoid tobacco products.
Stay hydrated to promote saliva production.
Wear a mouthguard during sports activities.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Schedule biannual professional cleanings and examinations to catch issues early before they become serious problems.
Conclusion
Dental pain can be distressing; however, understanding its causes and knowing how to respond can significantly improve your oral health journey. By following proper oral hygiene practices, making smart lifestyle choices, and leveraging the latest advancements in dental technology, you can maintain a healthy, pain-free smile.
Remember that while this guide provides valuable information, it is not a substitute for professional dental care. If you’re experiencing persistent or severe dental pain, consult with a dental professional promptly. Take charge of your oral health today—and smile with confidence tomorrow!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the most common causes of dental discomfort?
- Common causes include tooth decay, gum disease, dental injuries, enamel erosion, and infections.
Can dental discomfort indicate a serious health issue?
- Yes! Persistent or severe dental pain—especially if accompanied by fever or swelling—can indicate an underlying serious condition requiring immediate medical attention.
How can I prevent dental discomfort?
- Good oral hygiene practices like regular brushing and flossing combined with a balanced diet low in sugars are crucial for prevention.
What should I do if I experience sudden severe dental pain?
- Seek immediate dental care if you experience severe pain along with symptoms like swelling or fever as these could signal serious issues.
Are home remedies effective for dental discomfort?
- Home remedies like warm saltwater rinses can provide temporary relief but should not replace professional care for severe or persistent problems.